Breathtaking Tips About What Does 208 230V Mean

Decoding 208/230V
1. Understanding Voltage in Plain English
Ever stared at an appliance label and seen "208/230V" and felt a sudden urge to back away slowly? Don't worry, you're not alone! Electrical jargon can be intimidating, but breaking it down is actually quite simple. Basically, these numbers are telling you the voltage that the appliance needs to operate properly. Voltage is, in a nutshell, the electrical "push" that gets the current flowing. Think of it like water pressure; higher voltage, stronger flow.
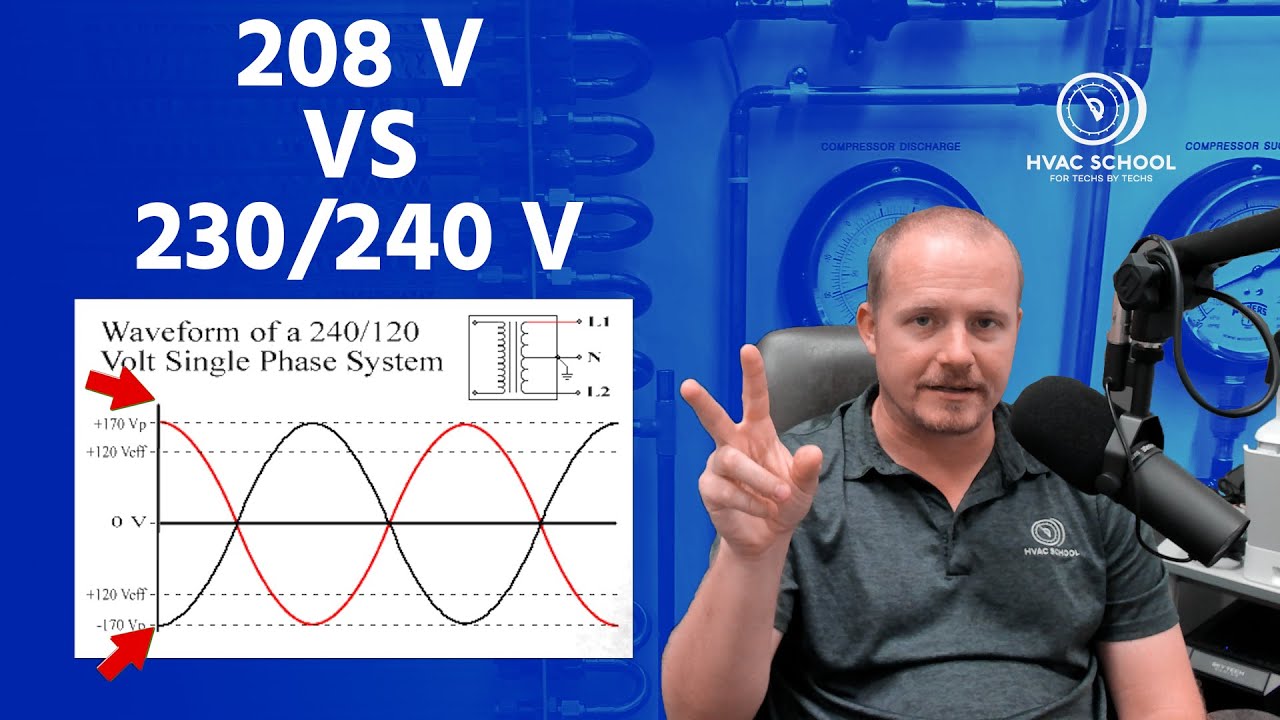
Now, why two numbers? That's where things get a little more interesting. In many commercial and industrial settings, you'll find 208V electrical systems. These are derived from a three-phase power setup, which is more efficient for large loads. Residential areas, on the other hand, typically use 230V (though you might also see 240V, which is close enough). The appliance is designed to work safely and efficiently within that range, hence the "208/230V" rating. It's like saying a car gets good gas mileage between 55 and 65 mph; it's designed to perform best within that specific range.
The key takeaway here is compatibility. You need to make sure the appliance's voltage requirement matches the voltage supplied by your electrical system. Plugging a 208V appliance into a 230V outlet (or vice versa) can lead to problems, ranging from poor performance to potential damage — or even a fire hazard, which is definitely something we want to avoid! So, always check the labels and consult a qualified electrician if you're unsure. Electricity is a powerful tool, but it demands respect.
Think of it this way: imagine trying to run a marathon while wearing flip-flops. Sure, you could try, but it's not going to be pretty. You'll likely tire out quickly, and your feet will be screaming in agony. Similarly, mismatching voltage can strain the appliance and lead to premature failure. Therefore, confirming the voltage compatibility is a vital step to protect your electronics and your own safety.

Why the Difference? Delving Deeper into Electrical Systems
2. Exploring Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Okay, let's nerd out on electricity for a moment (but only a moment, I promise!). The reason we have different voltage levels, like 208V and 230V, boils down to the way power is distributed. Most homes use what's called "single-phase" power. Think of it as a single lane highway for electricity. It's simpler and cheaper to set up, which makes it perfect for powering your lights, TV, and toaster.
Businesses and larger buildings, on the other hand, often use "three-phase" power. This is like a three-lane highway, providing a more efficient and stable power supply for heavier equipment like industrial machinery, air conditioners, and large refrigerators. The 208V system is a common byproduct of this three-phase setup. Without getting too technical, it allows for more efficient distribution of power across multiple circuits. It's all about balancing the electrical load and preventing things from overheating.
So, while your home might have a 230V outlet for your dryer or oven, a commercial building might have a mix of 120V, 208V, and 230V outlets, each serving different purposes. Thats why it is important to always inspect an appliance power requirements versus the supplied power. It's a bit like having different types of roads for different types of vehicles; a small car doesn't need a six-lane highway, and a semi-truck can't safely navigate a narrow country lane.
The system is designed to deliver power effectively for the purpose that a building has. A restaurant with many appliances that need a lot of power will benefit from having three-phase power supply. If you are still unsure of the type of electrical system you have or the power requirements of your appliances its best to contact an electrician. Not only can they keep you safe but they can provide you with the best setup for your building.

Difference Between 220 And 240 Volt Outlet
Spotting the Difference
3. Reading the Fine Print (and Why You Should!)
Alright, so how do you actually know what voltage an appliance needs? Thankfully, manufacturers are pretty good about labeling their products. You'll usually find the voltage requirement printed on a sticker or plate located on the back or bottom of the appliance. It might be near the power cord or inside the door (for appliances like refrigerators or ovens).
Look for something that says "Voltage," "V," or even just "Input." It should be followed by a number, or in our case, "208/230V." Pay close attention! This little label holds the key to a happy and functional appliance. Don't just assume that any outlet will do. It's like assuming that any key will open any door; it might work, but it's more likely to cause problems.
If you can't find a label, check the appliance's user manual. The manual should provide all the necessary technical specifications, including the voltage requirement. If you've lost the manual (we've all been there!), you can often find a digital version online by searching for the appliance's model number and "user manual." The internet is a treasure trove of information, even for dusty old appliances.
Consider this as well, some appliances might not have a specific voltage label. Rather they use a plug type that implies what voltage they can use. For instance, larger appliances that require more electricity might use a NEMA 14-50 plug that is compatible with 240V outlets. However, this isnt always the case so if you are unsure, contact an electrician to help identify your appliances voltage requirements.

What Happens When Things Go Wrong? Mismatched Voltage Nightmares
4. The Perils of Ignoring the Labels
Okay, so what happens if you ignore all this advice and plug a 208V appliance into a 230V outlet (or the other way around)? Well, it's not going to be a pretty picture. Plugging a 208V appliance into a 230V outlet can cause it to overheat and potentially burn out. It's like trying to force too much water through a pipe; eventually, something's going to burst.
On the other hand, plugging a 230V appliance into a 208V outlet might result in poor performance. The appliance simply won't get enough "push" to operate correctly. Your oven might take forever to preheat, or your air conditioner might not cool the room effectively. It's like trying to drive uphill in a car with a weak engine; you'll struggle to make progress.
In the worst-case scenario, a voltage mismatch can create a fire hazard. Overheating components can ignite nearby materials, leading to a potentially dangerous situation. That's why it's always better to be safe than sorry. If you're ever unsure about voltage compatibility, consult a qualified electrician. They can help you identify the correct voltage and ensure that your appliances are properly connected.
There is also the safety of the building to consider when using the wrong voltage. If an appliance that isnt compatible to the electrical system fails, it can damage the wiring and the building itself. In commercial spaces with sensitive equipment it is especially important to ensure voltage compatibility.

Staying Safe
5. Ensuring a Smooth Electrical Experience
So, how do you avoid these voltage-related headaches? Here are a few simple tips to keep in mind. First and foremost, always check the voltage requirements of any appliance before plugging it in. Make it a habit! It only takes a few seconds, and it could save you a lot of trouble down the road. Think of it as a pre-flight checklist for your electrical appliances.
If you're moving into a new home or building, take some time to identify the voltage of your electrical outlets. You can use a multimeter to measure the voltage, or consult a qualified electrician. Knowing your electrical landscape will help you make informed decisions about which appliances to buy and where to plug them in. It will also give you an idea of what to expect in the building regarding electricity.
Consider using a voltage regulator or surge protector, especially for sensitive electronics. These devices can help smooth out voltage fluctuations and protect your appliances from damage. They're like little bodyguards for your electrical equipment, shielding them from harm. A voltage regulator ensures a consistent flow of electricity while a surge protector kicks in to block any voltage spike that might come through during storms for instance.
Finally, when in doubt, always consult a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge and experience to handle any electrical situation safely and effectively. Don't try to be a DIY electrician unless you have the proper training and experience. Electricity is not something to be trifled with. The key is to be prepared by inspecting the type of electricity that a building uses and what the voltage requirements of the different appliances are.
FAQ
6. Clearing Up Common Confusions
Still scratching your head about voltage? Let's tackle some frequently asked questions:
Q: Can I use a 220V appliance in a 230V outlet?
A: Generally, yes. A 220V appliance is usually designed to operate safely within a range that includes 230V. However, always check the appliance's specifications to be sure. If there are any concerns you should contact an electrician to find out what the best solution might be.
Q: What happens if I accidentally plug the wrong voltage appliance in?
A: It depends. It might work poorly, overheat, or even be damaged. In the worst-case scenario, it could create a fire hazard. Unplug it immediately and consult an electrician.
Q: How can I tell if I have 208V or 230V outlets?
A: The easiest way is to use a multimeter to measure the voltage. You can also consult a qualified electrician. They can quickly identify the voltage and ensure that your electrical system is safe.
Q: Are 208V and 240V the same thing?
A: No, they are not exactly the same, although they are close. 208V is generally associated with a three-phase system while 240V comes from a single-phase system. An appliance compatible with both will be labeled as 208-240V.
Q: Can I convert a 208V outlet to a 230V outlet?
A: It's not a simple plug-and-play solution. Converting voltage requires rewiring and might not even be possible depending on your electrical system. Consult a qualified electrician for professional advice.