Unique Tips About Why Does AC Have Live And Neutral

Where Does The Neutral Wire Come From, Explained YouTube
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Why the Two-Wire Tango?
Ever wondered why your electrical outlets have those two (or sometimes three) slots? It's not just for symmetry, I assure you! Those slots are the gateways for what we call "live" (also known as "hot") and "neutral" wires in an alternating current (AC) system. Think of it as a carefully choreographed dance of electrons, where each wire has a crucial role to play.
The live wire is the energetic one, the life of the party, if you will. It carries the alternating voltage from the power source to your appliance. This voltage is what provides the electrical potential, the driving force, that makes your devices do their thing, whether it's brewing a cup of coffee, chilling your food, or powering your laptop.
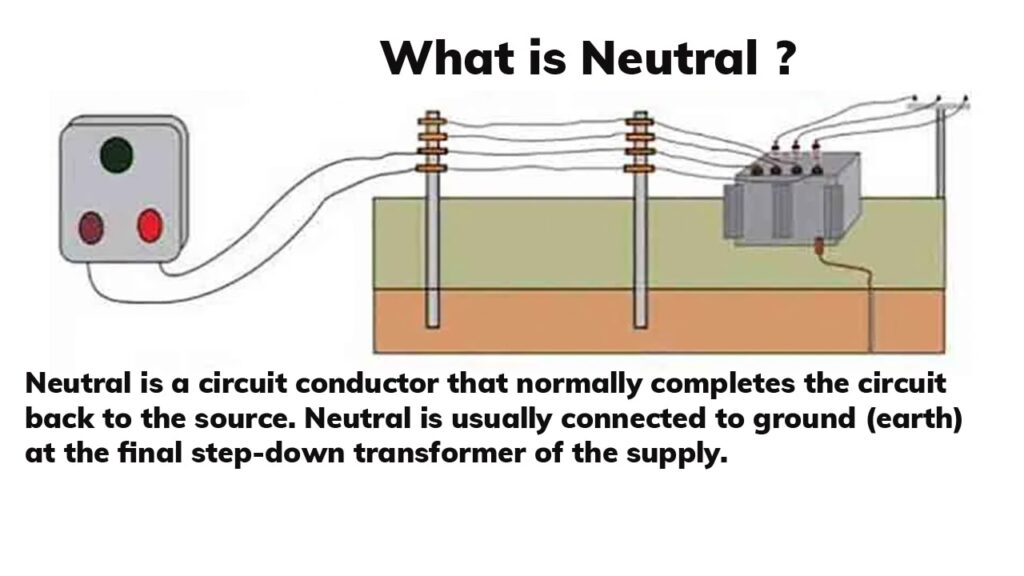
Now, the neutral wire is its partner in crime, the calm and collected one. It completes the circuit by providing a return path for the electrons back to the power source. Crucially, under normal circumstances, the neutral wire is kept at or near ground potential, meaning it has very little voltage compared to ground. This makes it safer to touch — although, let's be clear, you should never go around touching electrical wires! Safety first!
Without both the live and neutral wires, you wouldn't have a complete circuit, and your appliance wouldn't receive the electricity it needs. It's like trying to clap with only one hand — it just doesn't work. The interaction between these two wires is essential for the flow of electricity, forming the basis for how AC power functions in your home.

StepbyStep Guide How To Wire A 3 Phase Air Conditioner Wiring
AC
2. Why Not Just Stick With One Wire?
You might be thinking, "Why all this fuss about two wires? Why not just use one?" Well, that's because of the nature of AC power. AC stands for alternating current, which means the flow of electrons periodically reverses direction. This is different from direct current (DC), like what you get from a battery, where the electrons flow in one direction only.
The alternating nature of AC is what makes it so efficient for transmitting power over long distances. Power companies can use transformers to easily step up the voltage for transmission and then step it back down for use in your home. This is much more difficult to do with DC power. Having a neutral wire allows this alternating flow to happen smoothly and efficiently. It provides a stable reference point and a clear path for the electrons to return, no matter which direction they're flowing.
Imagine trying to drive a car without a return lane on the highway — chaos would ensue! The neutral wire is like that return lane, ensuring that the electrical traffic flows smoothly and safely. It's a key component in the AC power system that we rely on every day.
Without a well-defined neutral path, the fluctuating current could create unpredictable voltage drops and electromagnetic interference, potentially damaging appliances and causing all sorts of electrical mayhem. The neutral wire keeps everything in check and ensures a stable and reliable power supply.
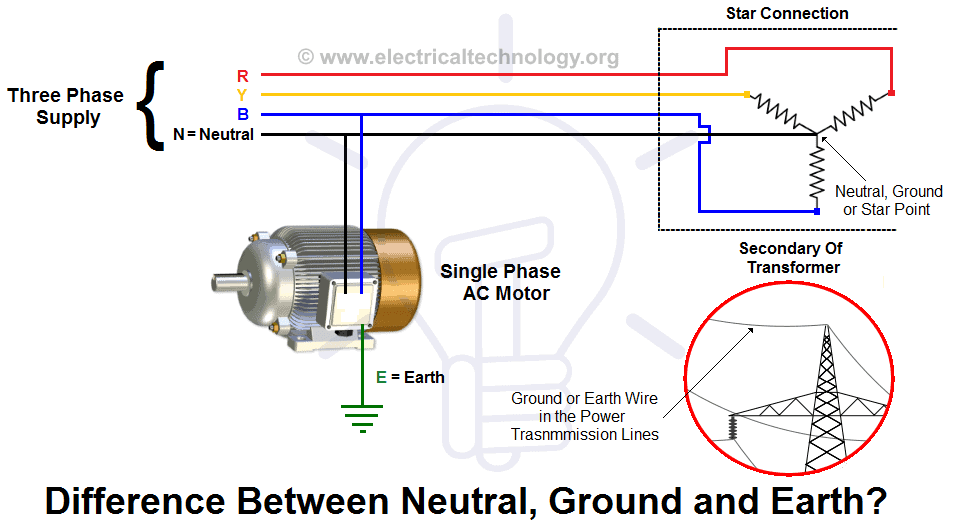
Grounding
3. Why the Extra Hole in Some Outlets?
Okay, so we've covered live and neutral, but what about that third hole in some outlets? That's for the ground wire! The ground wire is a safety feature that provides an alternate path for electricity to flow in case of a fault. It's connected to the earth (literally, through a grounding rod) and is designed to trip a circuit breaker or blow a fuse if there's a short circuit.
Think of the ground wire as a safety net. If a live wire accidentally comes into contact with the metal casing of an appliance, the ground wire provides a low-resistance path for the current to flow back to the source. This large current surge triggers the breaker, cutting off the power and preventing a potentially dangerous electric shock. It's all about safety first, folks!
Not all appliances need a ground wire. Double-insulated appliances, for example, have extra layers of insulation to prevent any contact between live wires and the casing. However, for appliances with metal casings, a ground wire is essential for protecting users from electric shock.
The ground wire doesn't carry current under normal circumstances. It's only there as a backup, a last line of defense against electrical hazards. It's like having a spare tire in your car — you hope you never need it, but you're sure glad it's there when you do.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-central-air-conditioners-1152645_V2-390c6f1f6ca14b4ebc59426f226a78a8.png)
How Hvac Systems Work Diagram
The Dance of Electricity
4. Putting It All Together
So, to summarize, the live wire brings the voltage, the neutral wire provides the return path, and the ground wire (when present) offers a safety net. Together, they form the foundation of the AC power system that powers our modern world.
Understanding the roles of these wires is not just for electricians. It can help you troubleshoot simple electrical problems, understand the importance of proper wiring, and appreciate the safety measures that are in place to protect you from electrical hazards. Knowledge is power, after all!
While electricity is incredibly useful, it's also important to remember that it can be dangerous. Always exercise caution when working with electricity, and if you're not comfortable, call a qualified electrician. Don't become a statistic! Electrical safety is paramount. Leave the complicated stuff to the pros.
Hopefully, this explanation has shed some light on the "live and neutral" mystery. It's a fascinating dance of electrons, all working together to keep our lights on and our devices humming. Appreciate the intricate system that brings power to your fingertips, and remember to always be safe!
Why 1.5 V To 3 Voltage Between Neutral & Earth Electrical
FAQ
5. Frequently Asked Questions
Still scratching your head about live, neutral, and ground? Here are a few frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion:
Q: What happens if I accidentally switch the live and neutral wires?A: While the appliance might still work, it's a very bad idea! Switching the live and neutral wires can create a shock hazard, as the appliance casing could become energized. Always ensure proper wiring for safety.
Q: Can I get shocked if I touch the neutral wire?A: Under normal circumstances, the neutral wire is at or near ground potential, so the risk of shock is low. However, it's never a good idea to touch any electrical wire without proper precautions. If there is a fault somewhere, touching the neutral wire can still shock you. Always err on the side of caution.
Q: Why are some outlets polarized (one slot wider than the other)?A: Polarized outlets are designed to ensure that appliances are connected with the live and neutral wires in the correct orientation. The wider slot is for the neutral wire, and the narrower slot is for the live wire. This helps prevent shock hazards by ensuring that switches and other safety features are connected to the live side of the circuit.
Q: My lightbulb keeps blowing. Could it be related to the live and neutral wires?A: Possibly. While a frequently blowing lightbulb could be due to a number of things, loose wiring or voltage fluctuations related to the live and neutral wires could be contributing factors. It's best to have an electrician check your wiring to rule out any underlying problems.
